Business Solutions
Shielding the Modern Fleet: Robust Vehicle Cybersecurity Strategies in the Age of Connectivity
In the age of smart vehicles and constant connectivity, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for fleet managers and car manufacturers alike. Modern vehicles are packed with advanced technology, making them both efficient and vulnerable to cyber threats. This blog dives into the importance of robust vehicle cybersecurity, exploring cutting-edge strategies to safeguard connected fleets against potential risks. Whether you oversee commercial fleets or personal vehicles, understanding these strategies is key to staying one step ahead of evolving cyber threats. Stay secure, stay connected, and take control of your vehicle’s safety!

The modern vehicle, a marvel of interconnected systems, is increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. As cars transform into rolling computers, a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is no longer optional—it’s imperative. OEMs must adopt a multi-layered approach to protect vehicles from evolving threats, encompassing everything from secure design principles to automated threat detection in the automotive cybersecurity sector.
Building Security In: The Foundation of a Robust Strategy
The first line of defense lies in embedding security into the vehicle’s architecture from the ground up. This involves:
Secure Design Principles: Implementing security by design, ensuring that security considerations are integrated into every stage of the development lifecycle. This includes threat modeling, vulnerability assessments, and secure coding practices.
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs): Utilizing dedicated hardware modules to protect sensitive cryptographic keys and perform secure operations. This provides a secure foundation for authentication, encryption, and other security functions.
Secure Communication Protocols: Employing robust communication protocols, such as encrypted CAN bus communication and secure Ethernet, to protect data transmitted within the vehicle’s network.
Secure Boot and Firmware Updates: Implementing secure boot mechanisms to ensure that ECUs boot from trusted firmware and utilizing secure over-the-air (OTA) update capabilities to patch vulnerabilities and deploy security enhancements.

Automated Threat Detection: TARA Cybersecurity and Beyond
As the complexity of vehicle systems increases, manual threat analysis becomes impractical. Automated threat detection, particularly through Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) for cybersecurity, is essential for proactive defense.
TARA Cybersecurity:
This methodology involves systematically identifying and assessing potential threats to the vehicle’s cybersecurity.
It uses automated tools to analyze system architectures, identify potential attack vectors, and assess the impact of potential attacks.
TARA enables manufacturers to prioritize security measures and allocate resources effectively.
This process should be continuously repeated throughout the vehicles life cycle, as new threats emerge.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS):
Deploying IDPS solutions that monitor vehicle networks for anomalies and suspicious activity.
These systems can use machine learning algorithms to detect subtle threats that traditional signature-based systems might miss.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
Centralizing security logs and events from various vehicle systems to provide a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s security posture.
SIEM systems can correlate events and identify patterns that indicate potential attacks.
Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing:
Regularly conducting automated vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify and address security weaknesses.
This proactive approach helps to discover vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
Beyond the Vehicle: A Holistic Approach
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy extends beyond the vehicle itself, encompassing the entire ecosystem:
Supply Chain Security: Ensuring that all components and software used in the vehicle are sourced from trusted suppliers and undergo rigorous security testing.
Cloud Security: Protecting data transmitted to and from the cloud, as well as securing cloud-based services used by the vehicle.
Incident Response: Developing a robust incident response plan to handle cybersecurity incidents effectively, including containment, eradication, and recovery.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Fostering collaboration and information sharing among manufacturers, suppliers, and cybersecurity experts to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Vehicle cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires a multi-faceted approach. By combining secure design principles, automated threat detection, and a holistic security strategy, manufacturers can help to protect vehicles from cyberattacks and ensure the safety and security of drivers and passengers in the connected age.
Business Solutions
RF Converters: How RF-to-Optical Converters Work in Modern RF Systems
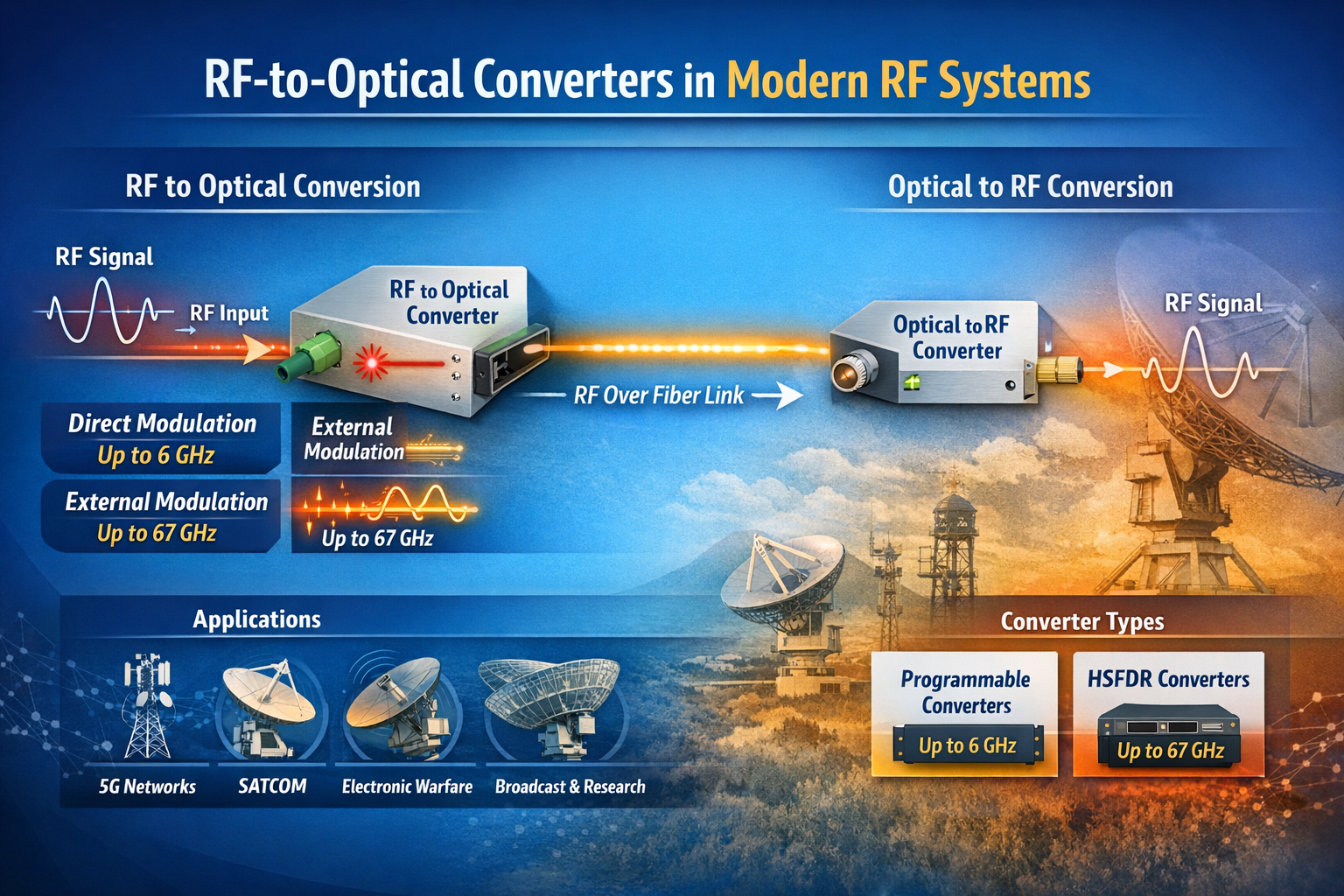
Introduction
The term “RF converter” encompasses a broad category of devices that change the form or frequency of an RF signal. In traditional RF engineering, an RF converter might refer to a frequency converter (mixer + local oscillator) that translates a signal from one frequency band to another. In the context of RF over fiber technology — a rapidly growing field — an RF converter specifically refers to a module that converts between the RF electrical domain and the optical domain.
This article focuses on RF-to-optical converters (and their optical-to-RF counterparts), the core building block of any RF over fiber (RFoF) system. We explain how they work, what parameters differentiate high-performance converters from commodity devices, and where they are used across today’s most demanding RF applications.
What Is an RF-to-Optical Converter?
An RF-to-optical converter — commonly called an RFoF transmitter module or RFoF Tx — is a device that accepts an RF electrical signal at its input and produces a modulated optical signal at its output. The conversion is achieved by using the RF signal to modulate the intensity (or phase) of a laser light source:
- Direct Modulation: The RF signal directly drives the bias current of a laser diode, modulating its output power. This approach is simpler and more compact, but has bandwidth limitations (typically up to 6–8 GHz) and higher relative intensity noise (RIN).
- External Modulation (Electro-Optic Modulation): A continuous-wave (CW) laser feeds a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) or other electro-optic device, which modulates the optical signal using the RF input. This approach supports much higher frequencies (up to 40 GHz, 67 GHz, and beyond) and achieves superior linearity and dynamic range.
The complementary device — the optical-to-RF converter, or RFoF receiver (Rx) — is a photodetector module that converts the incoming optical signal back into an RF electrical signal. Together, an Tx and Rx module form a complete RFoF link.
RF Converter Families: Programmable vs. HSFDR
In the RFoF market, RF converters are typically divided into two performance tiers:
Programmable RF Converters
Programmable RFoF converters use direct modulation laser technology and cover bandwidths from 1 MHz up to 2.5 GHz, 3 GHz, 4 GHz, 6 GHz, or 8 GHz. They are configurable via software (such as a USB-connected configuration tool) for gain, bias, and diagnostic parameters. RFOptic’s programmable RF converter family covers these bands and is widely used in GPS distribution, cellular DAS, public safety networks, and broadcast applications.
Key characteristics of programmable RF converters:
- Direct modulation technology — compact and cost-effective
- Configurable gain and bias via USB and software
- Suitable for bandwidths up to 6–8 GHz
- Diagnostic RF test of Tx, Rx, and end-to-end link
- Available in enclosed and OEM module form factors
High SFDR (HSFDR) RF Converters
High Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (HSFDR) RF converters use external electro-optic modulation to achieve superior linearity and frequency coverage. These converters are designed for applications where dynamic range and wideband performance are paramount — electronic warfare, radar, satellite communications, and 5G FR2 millimeter-wave testing.
HSFDR converters from RFOptic cover bandwidths from 100 MHz up to 20 GHz, 40 GHz, and 67 GHz, making them the appropriate choice when the application exceeds the frequency ceiling of direct modulation systems.
Key characteristics of HSFDR RF converters:
- External electro-optic modulation — highest linearity and frequency coverage
- Covers L, S, C, X, Ku, K, Ka, and V bands (up to 67 GHz)
- High SFDR — critical for multi-carrier and wideband signal transport
- Lower noise figure compared to direct modulation equivalents at high frequencies
- Available in benchtop, rack-mount, and OEM configurations
RF Converter Frequency Coverage: Market Comparison
Frequency range is the single most important differentiator between RFoF converter providers. While the mainstream market is well served by converters operating up to 3–6 GHz, the growth of mmWave 5G, Ka-band SATCOM, and broadband EW systems demands converters operating at 18 GHz, 40 GHz, and beyond.
| Max Frequency | Technology | Key Applications | Coverage Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 6 GHz | Direct modulation | GPS, DAS, public safety, C-band 5G | Standard |
| Up to 18 GHz | Direct / external modulation | X-band radar, wideband EW, Ku SATCOM | Mid-range |
| Up to 40 GHz | External modulation (EOM) | Ka-band SATCOM, mmWave 5G FR2, EW | High performance |
| Up to 67 GHz | External modulation (EOM) | V-band, EW/SIGINT, mmWave radar | Specialty / high-end |
RFOptic’s standard RF over fiber converter portfolio spans from the 2.5 GHz programmable tier all the way to a 67 GHz HSFDR product, providing a single-vendor solution across this entire frequency range. Details are available at rfoptic.com/standard-rf-over-fiber-links/.
Where Are RF Converters Used?
Cellular and 5G Networks
RF converters form the backbone of distributed antenna systems (DAS) and C-RAN (Cloud Radio Access Network) architectures, transporting RF signals from base stations to remote antenna locations over fiber. With 5G expanding into millimeter-wave (FR2) bands at 24–39 GHz, high-frequency RF converters are increasingly required for this market.
Satellite Communications Ground Stations
SATCOM ground stations use RF converters to transport IF and L-band signals from outdoor antenna equipment to indoor modem racks. High-frequency converters support the full IF range including Ka-band (26.5–40 GHz) and V-band without requiring downconversion — preserving signal fidelity and simplifying the signal chain.
Electronic Warfare and Defense
EW systems transport broadband RF signals from antenna arrays to signal processing hardware using RFoF converters. The key requirements are high SFDR, low noise figure, and wide frequency coverage. RFOptic’s EW & Radar solutions address these requirements with HSFDR converters covering L through V bands.
Test and Measurement
RF over fiber converters are used in antenna measurement ranges, EMC test chambers, and anechoic chambers to transport signals between the antenna under test and the measurement instrumentation. The fiber cable does not perturb the electromagnetic environment of the test chamber, unlike coaxial cable, which can act as an unintentional radiator.
Broadcast and Radio Telescope
Broadcast and scientific radio applications use RFoF converters to transport RF signals over long distances between antennas and processing centers. The low loss and wide bandwidth of fiber make it ideal for very long link distances where coaxial cable attenuation would be prohibitive.
Selecting the Right RF Converter
When choosing an RF converter for a specific application, engineers should evaluate:
- Frequency range: Does the converter cover the full operating band of your application, including any tuning range or harmonic considerations?
- Dynamic range (SFDR): Is the SFDR sufficient for the number of channels and signal levels in your system?
- Noise figure: What is the minimum detectable signal level? Is the converter’s NF compatible with your system noise budget?
- Form factor: Enclosed module, OEM PCB, benchtop, or rack-mount?
- Programmability: Do you need software-configurable gain and bias, or is a fixed design sufficient?
- Optical power budget: What fiber span and connector count will the link need to support?
- Remote management: Is SNMP, REST API, or HTML-based remote monitoring required?
For a full overview of RF over fiber converter products and applications, visit rfoptic.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an RF converter in the context of RF over fiber?
In RF over fiber systems, an RF converter refers to the transmitter module (Tx) that converts an RF electrical signal into a modulated optical signal, or the receiver module (Rx) that converts the optical signal back to RF. Together, they form a complete RF-to-optical-to-RF conversion link over fiber cable.
What is the difference between a programmable RF converter and an HSFDR converter?
Programmable RF converters use direct modulation laser technology, covering bandwidths up to 6–8 GHz, and are configurable via software for gain and bias settings. HSFDR (High Spurious-Free Dynamic Range) converters use external electro-optic modulation, covering frequencies up to 67 GHz, and are optimized for high linearity and dynamic range in demanding defense, SATCOM, and test & measurement applications.
What frequency range do RF-to-optical converters support?
Standard RFoF converters cover 1 MHz to 6 GHz. High-performance RF converters using external electro-optic modulation, such as RFOptic’s HSFDR product family, support frequencies up to 67 GHz — covering L, S, C, X, Ku, K, Ka, and V bands in a single product line.
Can RF converters support bidirectional RF signals?
Yes. Most RFoF systems support bidirectional operation using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) to separate the uplink and downlink signals on a single fiber. Some systems use a separate fiber for each direction. The configuration depends on the system’s wavelength plan and the WDM components available.
Where can I find technical datasheets for RF over fiber converters?
RFOptic provides technical specifications and datasheets for its full range of RF converters at rfoptic.com/standard-rf-over-fiber-links/. Specifications include frequency range, link gain, noise figure, SFDR, and optical power budget for each product in the programmable and HSFDR families.
Business Solutions
Drone-UAV RF Communication: The Backbone of Modern Aerial Operations
Drone-UAV RF Communication is revolutionizing the way drones operate, serving as the foundation for reliable, efficient, and innovative aerial systems. From ensuring seamless connectivity to enabling advanced maneuvers, this technology plays a pivotal role in modern drone operations. Its ability to provide consistent and secure communication is what makes it indispensable for both commercial and defense applications.

Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have become a pivotal technology across industries such as defense, agriculture, logistics, and surveillance. At the core of a drone’s functionality is its communication system, which enables control, data transfer, and situational awareness. Radio Frequency (RF) communication plays a crucial role in ensuring that UAVs can operate effectively in a variety of environments, with high reliability and low latency. Learn more about DRONE-UAV RF COMMUNICATION.
This article delves into the significance of RF communication in Drone-UAV operations, the challenges it presents, the technologies involved, and how future advancements are shaping the communication systems for UAVs.
The Role of RF Communication in Drone-UAV Operations
RF communication is the medium through which most drones communicate with ground control stations (GCS), onboard systems, and other UAVs in a network. It enables the transmission of various types of data, including:
Control Signals: These are essential for operating the UAV, including commands for takeoff, landing, navigation, and flight adjustments.
Telemetry Data: Real-time data on the UAV’s performance, including altitude, speed, battery level, and sensor readings.
Video and Sensor Data: Drones equipped with cameras or other sensors (such as thermal, LiDAR, or multispectral) require high-bandwidth RF communication to send video feeds or sensor data back to the ground station.
Learn more about Optical Delay Line Solutions.
Payload Data: UAVs used for specific tasks like delivery or surveillance may need to transmit payload-related data, such as GPS coordinates, images, or diagnostic information.
Given the variety of data types and the need for real-time communication, a robust and reliable RF communication system is essential for the successful operation of drones in both civilian and military applications.

RF Communication Technologies for Drone-UAVs
The communication requirements of drones are diverse, necessitating different RF communication technologies and frequency bands. These technologies are designed to address challenges such as range, interference, data rate, and power consumption.
1. Frequency Bands
The RF spectrum is divided into several frequency bands, and each is used for different types of communication in UAV systems. The most commonly used frequency bands for drone communications are:
2.4 GHz: This band is one of the most popular for consumer-grade drones. It offers a good balance of range and data transfer speed, although it is prone to interference from other wireless devices (such as Wi-Fi routers and Bluetooth devices).
5.8 GHz: This band is often used for high-definition video transmission in drones, as it offers higher data rates than 2.4 GHz, but with a slightly shorter range. It’s less crowded than 2.4 GHz and typically experiences less interference.
Sub-1 GHz (e.g., 900 MHz): This frequency is used for long-range communications, as lower frequencies tend to travel farther and penetrate obstacles more effectively. It’s ideal for military drones or those used in remote areas.
L, S, and C Bands: These bands are used in military and commercial UAVs for long-range communication, often for surveillance, reconnaissance, and tactical operations. These frequencies have lower susceptibility to interference and are better suited for higher-power transmissions.
2. Modulation Techniques
The RF communication system in drones uses different modulation techniques to efficiently transmit data. Modulation refers to the method of encoding information onto a carrier wave for transmission. Some common modulation techniques used in UAV RF communication include:
Frequency Modulation (FM): Often used in control signals, FM is simple and efficient, providing clear communication with minimal interference.
Amplitude Modulation (AM): Used for video and lower-bandwidth applications, AM transmits a signal whose amplitude is varied to carry the information.
Phase Shift Keying (PSK) and Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM): These more advanced techniques allow for high data transfer rates, making them ideal for transmitting high-definition video or large sensor datasets.
3. Signal Encoding and Error Correction
To ensure that RF communication remains stable and reliable, especially in noisy or crowded environments, drones use advanced signal encoding and error correction methods. These techniques help to mitigate the impact of signal interference, fading, and packet loss. Common methods include:
Forward Error Correction (FEC): This involves adding redundant data to the so that errors can be detected and corrected at the receiver end.
Diversity Reception: Drones may employ multiple antennas or receivers, allowing them to receive signals from different directions and improve the overall reliability of communication.
Spread Spectrum Techniques: Methods like Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) or Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) spread the signal over a wider bandwidth, making it more resistant to jamming and interference.
4. Long-Range Communication
For long-range missions, RF communication technology needs to go beyond traditional line-of-sight communication. To achieve this, drones can leverage various technologies:
Satellite Communication (SATCOM): When beyond-visual-line-of-sight (BVLOS) operations are required, drones can use satellite links (via L, S, or Ku-band frequencies) to maintain constant communication with the ground station.
Cellular Networks: 4G LTE and 5G networks are increasingly being used for drone communication, especially in urban environments. 5G, in particular, offers ultra-low latency, high-speed data transfer, and extensive coverage.
Mesh Networking: Some UAVs can form mesh networks where each drone communicates with others in the fleet, extending the range of the communication system and providing redundancy.
Challenges in Drone-UAV RF Communication
While RF communication is essential for UAVs, it presents several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the reliable and secure operation of drones.
1. Interference and Jamming
One of the biggest threats to RF communication in drones is interference from other electronic systems or intentional jamming. Drones, especially in crowded or military environments, must be capable of avoiding interference from various sources, such as:
Other drones operating on the same frequencies.
Wireless communication systems like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Intentional jamming by adversaries in conflict zones or hostile environments.
To mitigate these issues, drones use frequency hopping, spread spectrum techniques, and advanced error-correction algorithms to make communication more resilient.
2. Limited Range and Power Constraints
The effective range of RF communication in drones is limited by factors such as transmitter power, antenna design, and frequency band characteristics. While UAVs with longer ranges can use lower frequencies like 900 MHz or satellite links, they are often limited by battery life and payload capacity.
The trade-off between range and power consumption is an ongoing challenge. Drones must find a balance between maintaining communication and extending their operational flight times.
3. Security Risks
The RF communication channel is vulnerable to security threats, such as signal interception, spoofing, and hacking. Unauthorized access to the communication link could compromise the integrity of the UAV’s operations or allow malicious actors to take control of the drone.
To secure drone communications, encryption methods like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are employed, ensuring that only authorized parties can decrypt and interpret the transmitted data.
4. Latency and Data Throughput
For applications that require real-time control and feedback, such as autonomous drones or those used in first-responder scenarios, low-latency communication is crucial. High latency could delay mission-critical decisions, especially in dynamic environments like search and rescue operations or military engagements. Additionally, high-data-throughput applications like video streaming require RF systems with robust bandwidth management.
Future Trends in Drone-UAV RF Communication
As UAV technology continues to advance, so will the communication systems that power them. Key trends in the future of drone RF communication include:
5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks is expected to revolutionize drone communications with ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and greater network density. This will enable more drones to operate simultaneously in urban environments, enhance remote operation, and facilitate advanced applications such as drone swarming and real-time video streaming.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Dynamic Communication: AI-powered algorithms can optimize communication links based on environmental conditions, such as avoiding interference, adjusting frequencies, and ensuring maximum data throughput. AI will also play a role in improving autonomous decision-making for UAVs in communication-heavy operations.
Integration with IoT: Drones are increasingly integrated into the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. As a result, drones will not only communicate with ground control but also with other devices and systems in real-time. This opens new possibilities for industrial applications like smart farming, precision delivery, and environmental monitoring.
RF communication is at the heart of every drone’s operation, whether for military, industrial, or commercial use. As UAV technology continues to evolve, so too must the communication systems that support them. RF communication technologies are enabling drones to perform increasingly complex tasks, from surveillance and reconnaissance to logistics and environmental monitoring.
Despite the challenges posed by interference, range limitations, and security risks, advances in RF technology, coupled with innovations like 5G and AI, promise to take UAV communication systems to new heights—fostering more reliable, secure, and efficient operations across a range of industries.
Business Solutions
OTP Verification at Scale with VoIP Smart Support
Effortlessly manage OTP Verification at scale with VoIP Smart Support. Experience secure, reliable, and efficient solutions designed to meet the demands of growing businesses. Simplify authentication and enhance user trust. Discover how VoIP Smart Support can elevate your verification process today!

Why Secure Access Needs Smarter Infrastructure
Every second, thousands of users worldwide are receiving one-time passwords to log in, confirm a transaction, or recover access to their accounts. But as digital engagement increases, the flaws in conventional delivery systems are becoming impossible to ignore. Delays, failed messages, and spoofed calls are undermining trust. That’s why scaling an OTP verification service now demands more than basic connectivity—it requires intelligent routing, redundancy, and optimization. Enter VoIP smart technology.
VoIP smart systems are transforming how one-time codes are delivered at scale, offering real-time, programmable, and efficient voice-based alternatives that ensure the code always reaches its destination, regardless of region or network barriers.
What Makes an OTP Verification Service Work?
At its core, an OTP verification service revolves around speed, precision, and trust. Users expect their one-time passwords to arrive immediately—usually within a few seconds—regardless of how or where they’re delivered. This is especially crucial in time-sensitive scenarios like banking logins, e-commerce checkouts, or account recovery.
An OTP system typically includes:
- A token generator to create time-limited codes
- A delivery mechanism (SMS, voice, or app)
- A validation module to check the input from the user
- A logic layer to handle retries, timeouts, and fallbacks
While SMS remains the most popular method, it’s no longer the most reliable—especially across regions with telecom restrictions, low infrastructure coverage, or aggressive message filtering. That’s where smarter alternatives like voice-based delivery come in, backed by intelligent VoIP infrastructure.

The Weak Spots in Traditional OTP Delivery
Many companies stick with SMS OTP because it’s familiar. But familiarity doesn’t guarantee performance. In reality, SMS delivery can be disrupted by:
- Carrier-level A2P (application-to-person) message filtering
- Regulatory hurdles like DND lists and local restrictions
- SIM swapping and spoofing attacks
- Latency due to congested telecom gateways
Worse, there’s minimal visibility when something fails. Delivery receipts are inconsistent, and troubleshooting is often reactive. The result? Lost users, failed logins, and poor brand experience.
By integrating VoIP smart solutions into your OTP verification service, you build resilience into the authentication process, especially in regions with high SMS failure rates.
Enter VoIP Smart: More Than Just Internet Calling
VoIP—short for Voice over Internet Protocol—has long been associated with internet-based calling. But VoIP smart takes it a step further by layering in programmable logic, intelligent routing, and real-time performance optimization.
Instead of simply placing a call, a smart VoIP system evaluates the best route, analyzes delivery quality in real time, and adapts on the fly. It can detect if a number is unreachable and retry through an alternate channel or carrier.
This intelligence is exactly what an enterprise-scale OTP verification service needs. It turns voice OTP delivery from a blunt fallback option into a strategic channel—capable of outperforming SMS in reliability and reach.
How VoIP Smart Transforms OTP Voice Delivery
Voice OTP delivery works by placing an automated call to the user and delivering the code through either a text-to-speech engine or a pre-recorded message. In areas where SMS fails or where regulations limit message delivery, voice calls offer a powerful backup—or even a preferred channel.
VoIP smart platforms enable:
- Dynamic voice scripts that adapt based on user language or location
- Region-aware call routing to minimize latency
- Real-time monitoring of call quality and delivery outcome
- Failover logic that automatically retries through alternate VoIP carriers
In markets like India, Indonesia, and parts of Africa, voice OTP often achieves higher delivery rates than SMS due to fewer telecom constraints. Plus, it’s harder for malicious actors to spoof or intercept voice calls compared to SMS messages.
Speed, Scalability, and Smart Logic
As demand grows, so does the need to handle massive OTP volume—often peaking during events like sales, product launches, or banking hours. A static, linear delivery system won’t hold up. What you need is a system that can auto-scale, adapt, and route intelligently.
VoIP smart APIs are built for this kind of elasticity. They offer features like:
- Load balancing across multiple data centers and carrier routes
- Prioritization of OTP traffic during peak loads
- Pre-configured retry logic based on call outcomes
- Real-time queue adjustments and rate control
This level of control is what makes scaling a global OTP verification service not just possible, but sustainable.
Using VoIP smart to support OTP services ensures your system scales seamlessly under pressure without sacrificing delivery reliability.
Security Boosts from Smarter VoIP Systems
OTP systems are often targeted by fraudsters, who attempt interception, redirection, or social engineering. A poorly configured delivery system can become a vulnerability. Smart VoIP solutions reduce this risk by introducing advanced call security features.
For instance:
- Caller ID masking ensures the OTP appears from a known, verified number
- Token-level encryption ensures only the intended recipient can decrypt the code
- Fraud detection algorithms can block suspicious patterns (like mass retries or number spoofing)
- Call verification logs give audit trails for compliance and dispute resolution
With VoIP OTP, it’s also easier to detect patterns that deviate from user norms—helping to trigger step-up authentication or session blocking when needed.

Hybrid Verification: SMS + Smart VoIP Fallback
The most resilient systems aren’t single-channel—they’re layered. A hybrid strategy blends SMS, smart VoIP, and even in-app push notifications to ensure that no matter what, the user gets their code.
Here’s how it might work:
- Send OTP via SMS.
- If not delivered within 5 seconds, trigger VoIP call with the same code.
- If both fail, offer in-app push or prompt email fallback.
With VoIP smart support, the fallback process becomes invisible and automatic, increasing the overall success rate of code delivery.
Customization and Branding in VoIP OTP Calls
Security doesn’t have to sound robotic. With smart VoIP platforms, you can add a personalized, branded voice to your OTP calls—improving both trust and user experience.
Features include:
- Custom intros (“This is a security call from [Brand Name]”)
- Multilingual voice synthesis
- Dynamic script insertion (e.g., “Your login code for [App] is 482901”)
- Branded caller ID for greater recognition
When users receive consistent, well-branded calls, they’re less likely to drop or ignore the message. That’s critical for first-time logins or sensitive transactions.
Compliance, Costs, and Carrier Interoperability
Operating globally means dealing with vastly different telecom environments. Some carriers restrict certain kinds of traffic. Others charge premium rates or limit the number of messages sent in a window. Staying compliant across this fragmented landscape is no small feat.
VoIP smart platforms are often better positioned to navigate this complexity. They include:
- Automatic compliance with local telephony laws (TRAI, GDPR, TCPA, etc.)
- Per-country call configuration and adaptive rate-limiting
- Cost optimization via dynamic least-cost routing
- Built-in blacklisting, whitelisting, and country restrictions
Smarter Pipes for Safer Passwords
Authentication is only as strong as the channel delivering it. In a world where security threats evolve daily and user expectations are sky-high, real-time delivery of one-time passwords is no longer a nice-to-have—it’s mission-critical.
VoIP smart technology provides the flexibility, performance, and intelligence that modern OTP verification services need to scale globally and perform reliably. It turns static voice delivery into a dynamic, secure, and user-friendly channel, closing the gap between intention and action.
To future-proof your authentication stack, it’s time to add VoIP smart capabilities into your OTP verification service—and ensure your users never wait for a code again.
FAQs
- What is a VoIP smart system?
A VoIP smart system is an advanced Voice over IP platform with intelligent features like programmable routing, real-time call monitoring, dynamic failover, and integration with APIs, making it ideal for time-sensitive services like OTP delivery.
- How does a VoIP smart system improve OTP delivery?
It ensures faster and more reliable OTP delivery by optimizing call routes, adapting to network conditions in real time, and providing fallback options when SMS fails.
- Why is voice-based OTP a good alternative to SMS?
Voice OTPs are less susceptible to message filtering and can reach users even in regions with unreliable SMS delivery or strict telecom regulations.
- Can VoIP smart solutions scale with high OTP demand?
Yes, VoIP smart platforms are built to handle large volumes of OTP traffic with features like load balancing, auto-scaling, and geo-distributed routing.
- Is VoIP OTP delivery secure?
Absolutely. Features like caller ID masking, encrypted tokens, and fraud detection protocols help ensure secure and trustworthy OTP voice calls.
- What happens if both SMS and VoIP OTP fail?
A hybrid OTP system using VoIP smart logic can trigger additional channels like push notifications or email, ensuring multi-layered delivery reliability.
- Can VoIP OTP calls be customized?
Yes. You can use custom voice scripts, brand identification, and language localization to improve user recognition and trust in the verification process.
-
3D Technology3 years ago
3D Scanner Technology for Android Phones: Unleashing New Possibilities
-
Business Solutions2 years ago
Understanding A2P Messaging and the Bulk SMS Business Landscape
-

 Business Solutions2 years ago
Business Solutions2 years agoThe Power of Smarts SMS and Single Platform Chat Messaging
-

 Automotive3 years ago
Automotive3 years agoDSRC vs. CV2X: A Comprehensive Comparison of V2X Communication Technologies
-
Tech3 years ago
On Using Generative AI to Create Future-Facing Videos
-

 Business Solutions2 years ago
Business Solutions2 years agoExploring OTP Smart Features in Smart Messaging Services
-

 Business Solutions2 years ago
Business Solutions2 years agoLive Video Broadcasting with Bonded Transmission Technology
-

 Business Solutions10 months ago
Business Solutions10 months agoThe Future of Healthcare SMS and RCS Messaging







